Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) background
For the past 30 years, the firms’ focus on how to improve the sustainability to produce a dynamic balance among economic, environmental and social aspects has been rapidly increasing. Acting on sustainability requires organizations to consider an integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices into their business management.
• What is ESG?
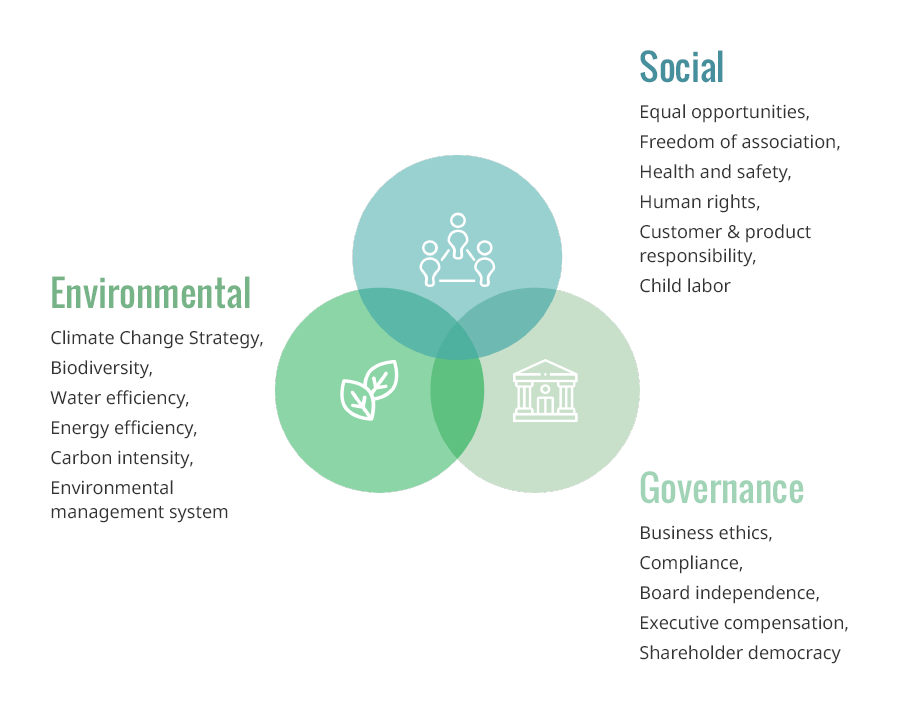
ESG is a subset of non-financial performance indicators which are used to assess sustainability commitments of a firm.
E – Environmental aspect: indicates how firms use their energy and manage their environmental impacts of business activities along the value chain.
S – Social aspect: emphasizes on stakeholder value creation. Taking care of employees, clients, and communities’ well-being, creating a fair and safe workplace, and having a respectful supply chain process are some examples of social part of the ESG framework.
G – Governance aspect: includes the system of controls, practices, and procedures to govern and make effective decisions, ensure transparency, business ethics, and regulative compliance.
• Why is ESG important?
Favorable environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices have become a way to support companies’ financial performance and their ability to grow and compete.
It is evident that there is an increasing number of financial institutions incorporating ESG rules into their funding criteria. It implies that firms which have successfully implemented sustainability and ESG strategies tend to be more appealing to investors.
Furthermore, by developing robust sustainability and ESG strategies, companies manage to overcome the increasing regulatory pressure and trading requirements regarding their social responsibility and their emissions to air, water and soil. It, therefore, helps the company attract more customers and build stronger community relations.
Attract Investors
Increasing numbers of investors integrates ESG considerations into their investment decisions.
Overcome
Regulatory Pressure
Requiring business to meet stricter quality demands and oblige to protect environment.
Meet Stricter
Buyer Requirements

Major brands and international chains are restructuring their global supply chains to meet their strict sustainability targets.
Attract Customers
Consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable products and change consumption behavior.
How can solar improve your ESG performance?
• ESG Impact
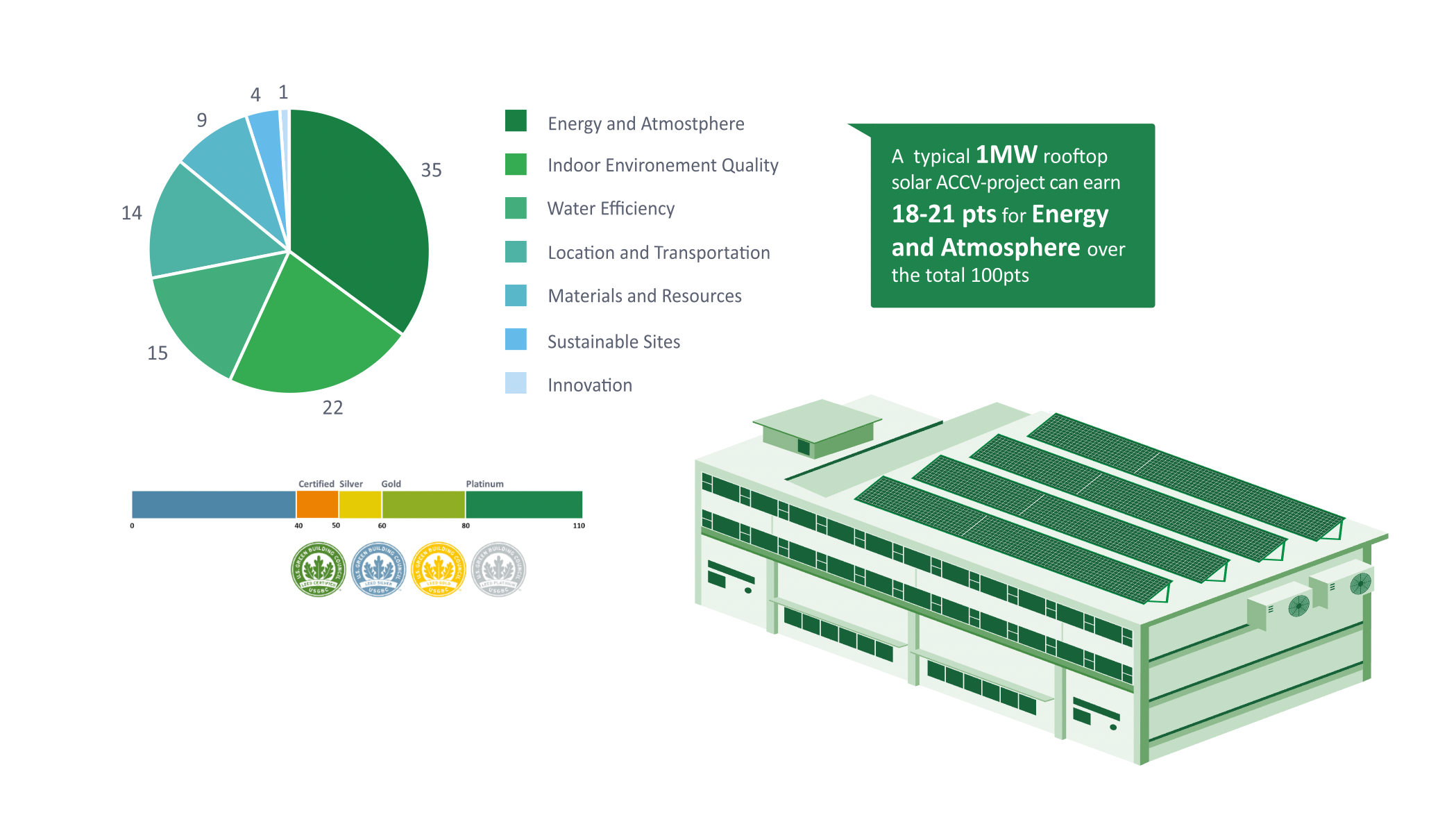
By using clean energy with solar in their daily operations, firms are supporting a positive and progressive energy transition. This enables firms to fulfill ESG objectives or sustainability initiatives with impact criteria, and gives firms access to green building certifications such as LEED certificates.
Environmental Benefits of Solar
Reduce carbon and water footprint
Displace fossil fuels
Mitigate climate change
Social Benefits of Solar
Strengthen local community resilience with local energy supply
Raise environmental awareness
Create economic opportunities
Governance Benefits of Solar
Enhance energy security
Reduce compliance costs
Responsible energy sourcing